Parallel Optics, MPO/MTP, and the Future of High-Bandwidth Data Centers with Multi-Core Fiber
- Nguyen Tran Tien
- Sep 8, 2025
- 3 min read
The Bandwidth Challenge
Hyperscale data centers and AI clusters are pushing optical infrastructure to its limits. Traditional single-lane optical links—10G, 25G, or even 100G serial—are no longer sufficient to handle the exponential growth in east-west and north-south traffic. To meet this demand, the industry has widely adopted parallel optics, where multiple fibers carry signals simultaneously to achieve higher aggregate bandwidth.
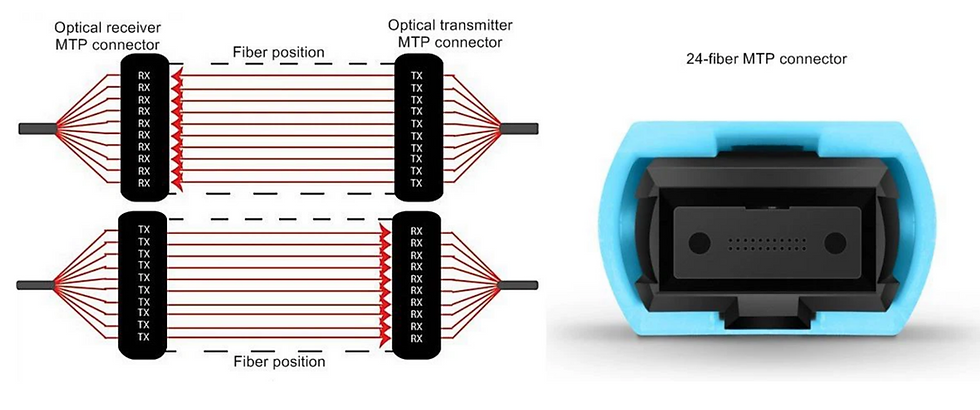
MPO/MTP: The Backbone of Parallel Optics
At the heart of parallel optics is the MPO/MTP connector, a high-density multi-fiber connector that allows 8, 12, 16, or even 24 fibers to be terminated in a single ferrule. Compared to traditional duplex LC connectors, MPO/MTP provides:
Massive Bandwidth Scaling: By transmitting data across multiple fibers in parallel, 40G, 100G, 200G, and 400G links become practical and cost-efficient.
Space and Cost Savings: One compact connector replaces multiple duplex connectors, reducing rack space and simplifying cabling.
Ease of Deployment: Pre-terminated MPO/MTP trunk cables can be quickly installed, reducing labor costs and improving reliability.
This combination of scalability, efficiency, and practicality has made MPO/MTP the default interface for modern parallel optics transceivers.
Transceiver Cost Advantage
A major factor behind the success of parallel optics is the cost efficiency of transceivers designed for MPO connections. Unlike traditional serial optics, which often require complex components such as multiplexers, demultiplexers, and high-precision lasers, parallel optics achieve high bandwidth simply by splitting the data stream across multiple fibers.
This architectural simplicity translates into:
Lower manufacturing complexity, resulting in more affordable transceiver units.
Better cost-per-bit performance, especially as speeds scale up.
A more economical choice for short- to medium-reach links inside data centers, where thousands of transceivers are deployed.
In short, parallel optics using MPO provides not just higher density, but also a significant reduction in overall transceiver costs, reinforcing its role as the preferred solution for scaling modern data center networks.
Enter Multi-Core Fiber (MCF)
While MPO/MTP solves the density problem at the connector level, Multi-Core Fiber (MCF) introduces density directly inside the fiber itself. Instead of a single optical core per fiber strand, MCF integrates 4, 8, or more cores into one standard 125 μm cladding.
When combined with MPO/MTP technology, MCF creates a powerful new paradigm:
Unprecedented Fiber Density: A 12-fiber MPO cable with 4-core MCF actually carries 48 optical channels—4× the throughput in the same footprint.
Lower Total Cost of Ownership: Less fiber volume means lower duct space usage, lighter weight, and reduced installation costs.
Future-Proof Scaling: MCF enables data centers to double or quadruple capacity without changing their cabling architecture. MPO/MTP connectors can be adapted to terminate fan-in/fan-out (FIFO) structures for MCF, ensuring compatibility with existing transceivers.
Applications in Data Centers
Intra-data center connections such as Top-of-Rack (ToR) to Leaf, Leaf to Spine, and even Data Center Interconnect (DCI) are prime candidates for MCF + MPO/MTP deployment. By leveraging parallel optics and multi-core technology together, hyperscale operators can achieve:
Higher throughput per rack with the same physical footprint.
Simpler cable management, avoiding the “spaghetti” problem of thousands of fibers.
Reduced capex and opex as infrastructure scales to support 800G and 1.6T Ethernet generations.
Conclusion
Parallel optics and MPO/MTP have already transformed data center networks by enabling cost-efficient, high-bandwidth transmission. The availability of lower-cost MPO-based transceivers makes this approach even more compelling compared to traditional duplex optics. Multi-Core Fiber (MCF) is the natural next step—amplifying the benefits of MPO/MTP by multiplying per-fiber capacity. Together, these technologies pave the way for the next generation of hyperscale and AI-driven data centers, where efficiency, density, and scalability define success.



Comments